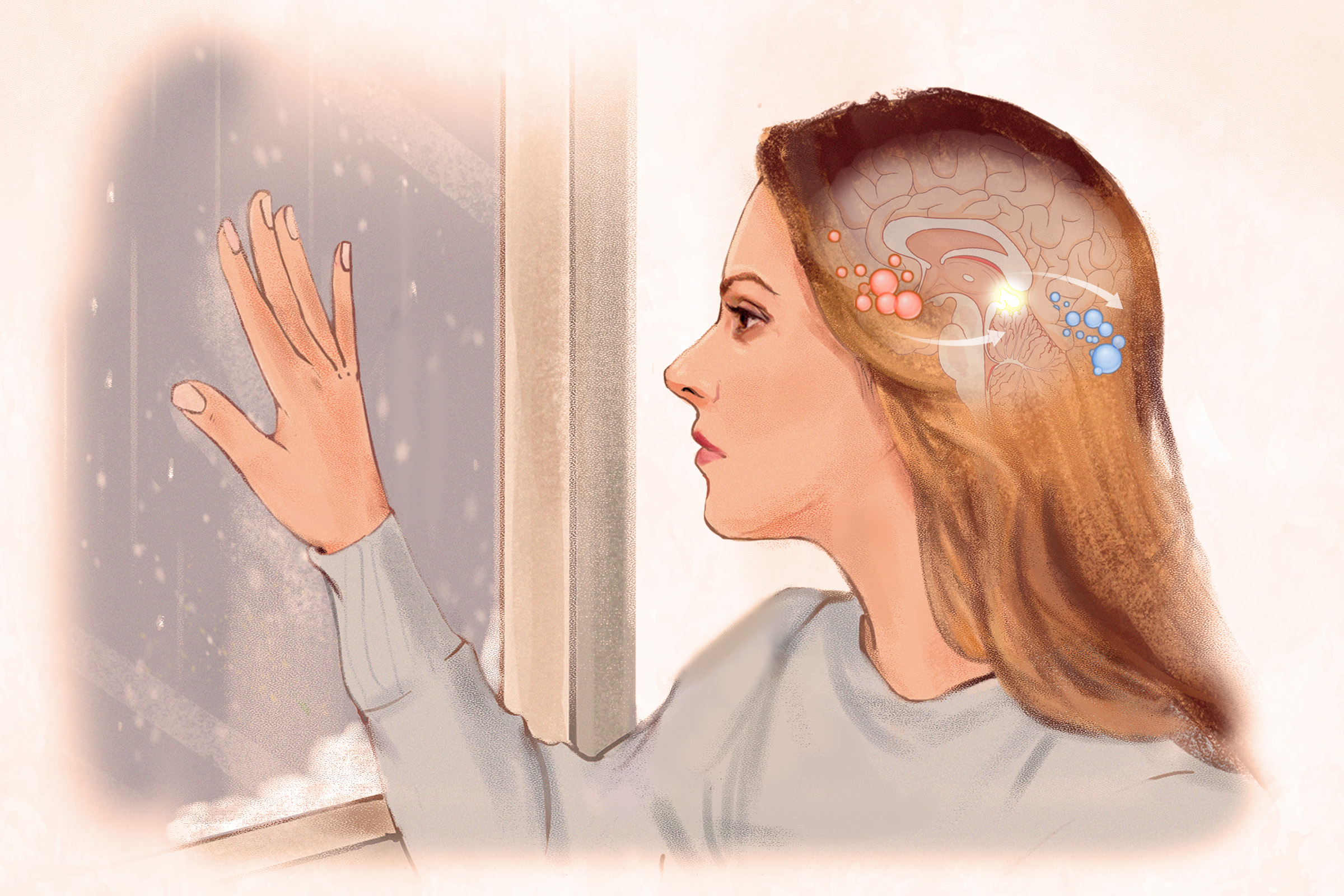
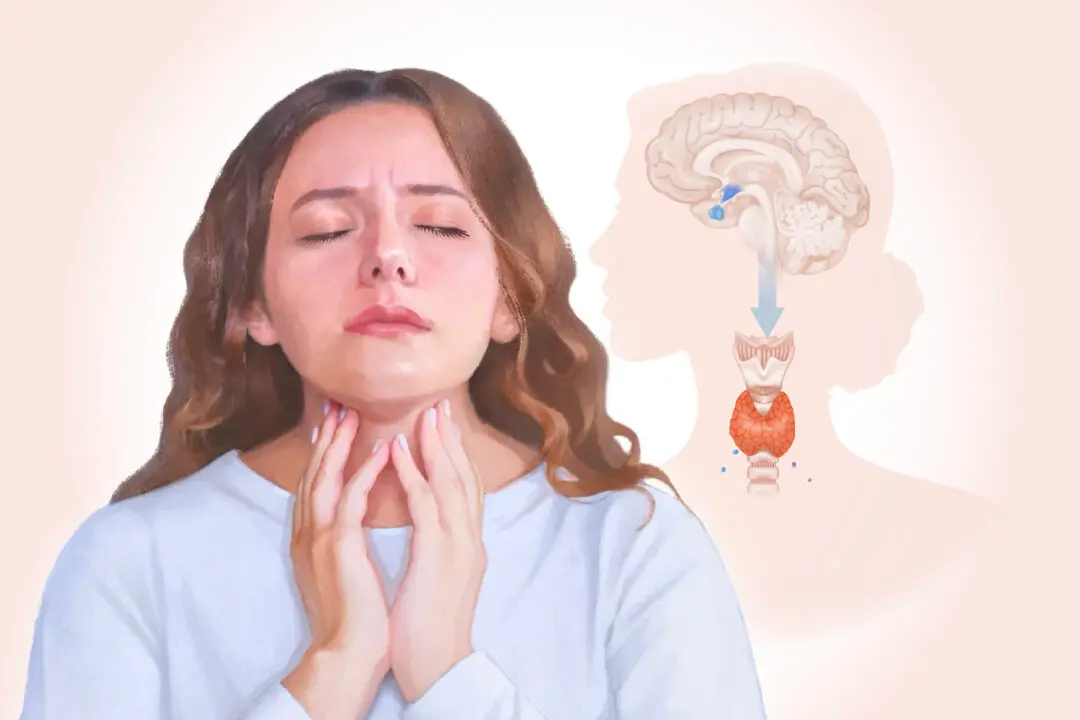
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD), also called seasonal depression, is a form of depression linked to specific times of the year, usually starting in fall or winter and improving in spring or summer. It is considered a subtype of major depression or bipolar disorder and is different from “winter blues.”
SAD is more common in areas farther from the equator due to reduced daylight exposure. In the United States, about 5 percent of adults experience SAD, with symptoms lasting nearly half the year.