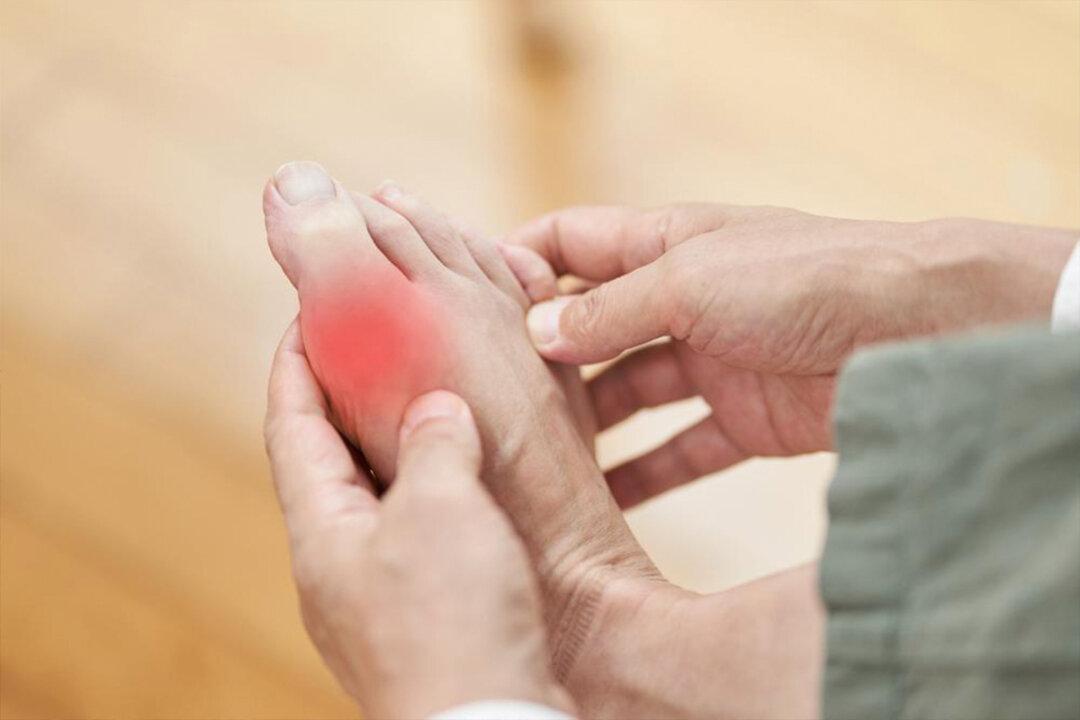
Gout is a common arthritis condition that often causes severe pain, swelling, and inflammation in joints at places such as the big toe, wrist, and knee. An estimated 9.2 million Americans suffer from gout, and it is more common among men and older people.
Gout is caused by too a buildup of uric acid in the body. Uric acid is a naturally occurring substance normally produced in the body and excreted through the kidneys. When the body cannot effectively pass enough uric acid, it can accumulate in the blood and form crystals, eventually causing gout attacks around the joints.
Possible Causes of Uric Acid Accumulation
Uric acid comes primarily from the decomposition of purine, which comes from food or is synthesized by the body. Uric acid buildup is likely caused by the following:- Genetics: Some people inherit genetic factors that make them more likely to produce too much uric acid or excrete it less efficiently, thus increasing their risk of gout.
- Diet: Excessive intake of purine-heavy foods, such as meat, seafood, alcohol, and beverages with added fructose, may lead to an increase in the production of uric acid and its accumulation in the body.
- Obesity: Obesity is also associated with an increased risk of gout because it affects uric acid excretion.
- Chronic diseases: Certain diseases such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease may affect the excretion of uric acid and thus increase the risk of its accumulation.
How to Prevent Gout
Gout attacks are excruciating and seriously affect the quality of life. You can try improving and managing your lifestyle and diet to prevent them. The following are some tips for doing that:- Diet adjustment: Eat less high-purine food and eat more low-purine food, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. Avoid alcohol, especially beer and strong spirits, as alcohol can accelerate the production and accumulation of uric acid.
- Weight control: Maintaining a healthy body weight and avoiding obesity can help reduce your risk of gout attacks. A study published in Arthritis Research & Therapy in 2021 found that weight gain is a significant risk factor for developing gout, especially weight gain in adulthood. The researchers emphasized that these findings highlight that maintaining a healthy body weight and weight loss across adulthood is essential for preventing and treating gout.
- Hydration: Adequate water intake can help enhance the excretion of uric acid and prevent its accumulation in the body. A study found a significant correlation between lower water intake and high levels of uric acid (hyperuricemia). After adjusting for age, gender, high blood pressure, and other factors, it was shown that people who drank more water had a 58 percent lower chance of developing hyperuricemia.
- Moderate exercise: Moderate exercise can help control weight and improve metabolism, helping to prevent gout.
- Appropriate medication: Doctors may recommend that patients take specific medications, such as uric acid-lowering drugs, to help lower uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks. Some of these drugs can have significant side effects.
- Avoiding stress and injury: Avoid excessive joint stress or injury to prevent gout attacks.