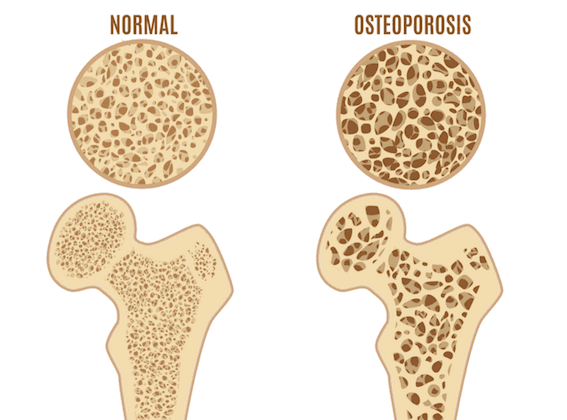
Osteoporosis is a systemic condition characterized by reduced bone mass and structural deterioration of bone microarchitecture, resulting in increased bone fragility and risk of fractures.
Sometimes described as a “silent epidemic,” osteoporosis has a high prevalence and high health care costs worldwide. With an aging population living longer than in the past, there is a growing incidence of osteoporosis and its complications, elevating it from a medical issue to a complex societal problem.
Signs and Symptoms
The clinical symptoms of osteoporosis primarily manifest as back pain, spinal deformity, and respiratory system issues, described as follows:- Back pain: Chronic lower back pain that tends to intensify when maintaining a fixed posture for an extended period, such as prolonged sitting or standing.
- Spinal deformity: Osteoporosis can lead to spinal deformity and reduced structural support. Vertebral compression can exacerbate kyphosis and shorten the distance between the rib cage and iliac crest, resulting in a hunched back. This symptom is characterized by an inability to lie flat and shortened spinal stature.
- Respiratory system issues: A deformed spine can cause the ribcage to press against the heart and lungs, resulting in symptoms such as chest tightness, shortness of breath, and respiratory difficulties. In severe cases, this can lead to pulmonary emphysema.