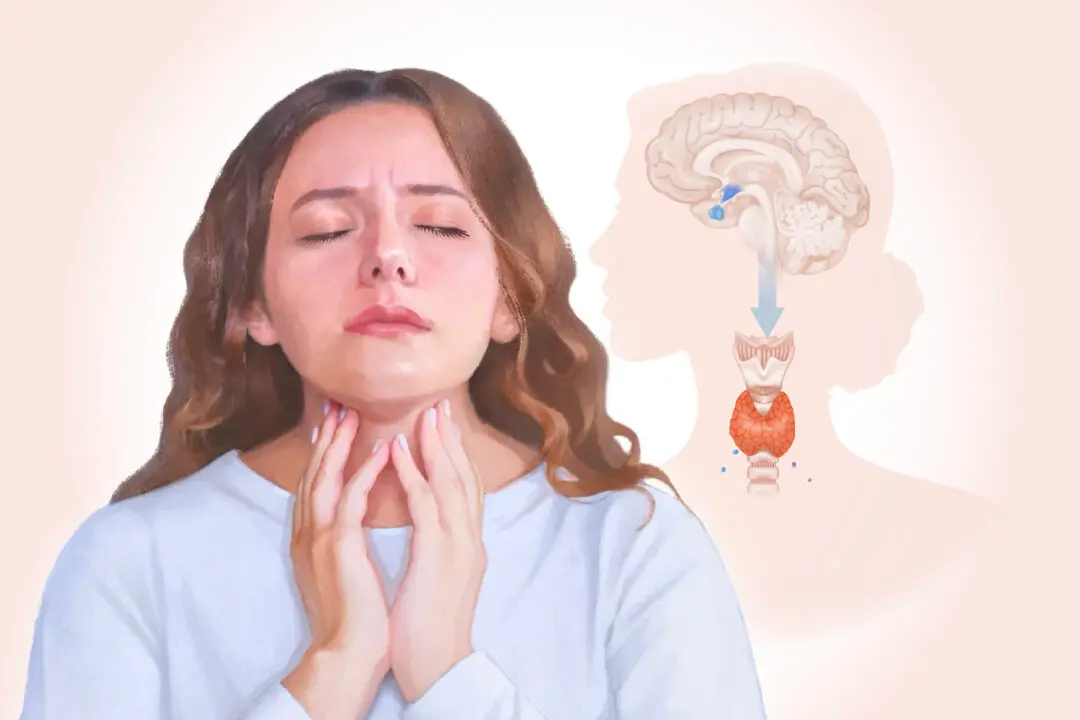
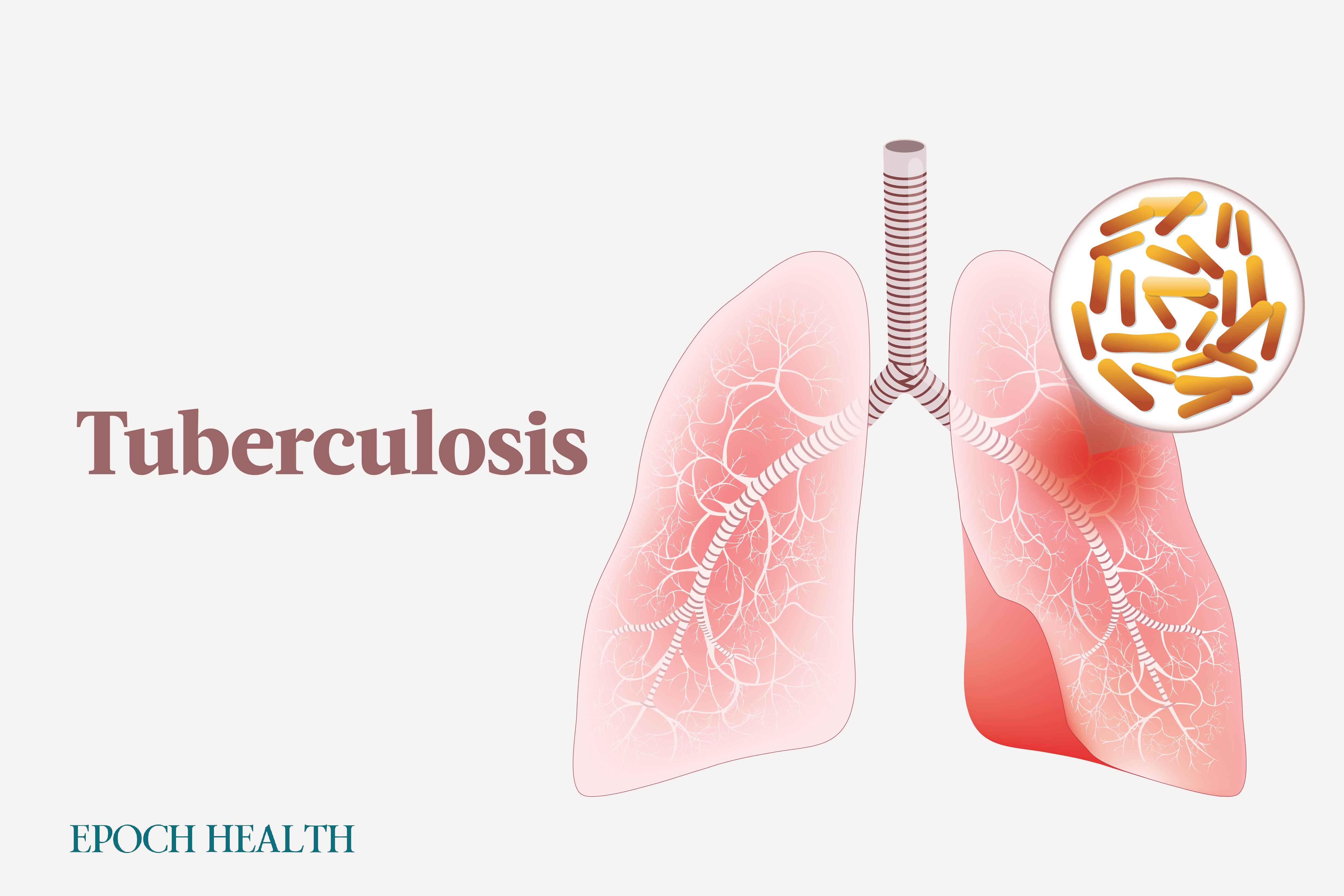
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious bacterial disease. Approximately 25 percent of the world’s population is believed to have contracted TB bacteria, with individuals infected having a 5 percent to 10 percent lifetime probability of developing active TB. The rest will live with latent TB.
In recent years, TB stood as the second most significant infectious cause of death globally, surpassed only by COVID-19. In 2022, an estimated 10.6 million people worldwide experienced TB, and 1.3 million died. In 2021, the United States recorded nearly 8,000 cases of TB. The most recent data on TB-related deaths in America are from 2020, when 600 people succumbed to the disease, corresponding to a mortality rate of 0.2 deaths per 100,000 persons.