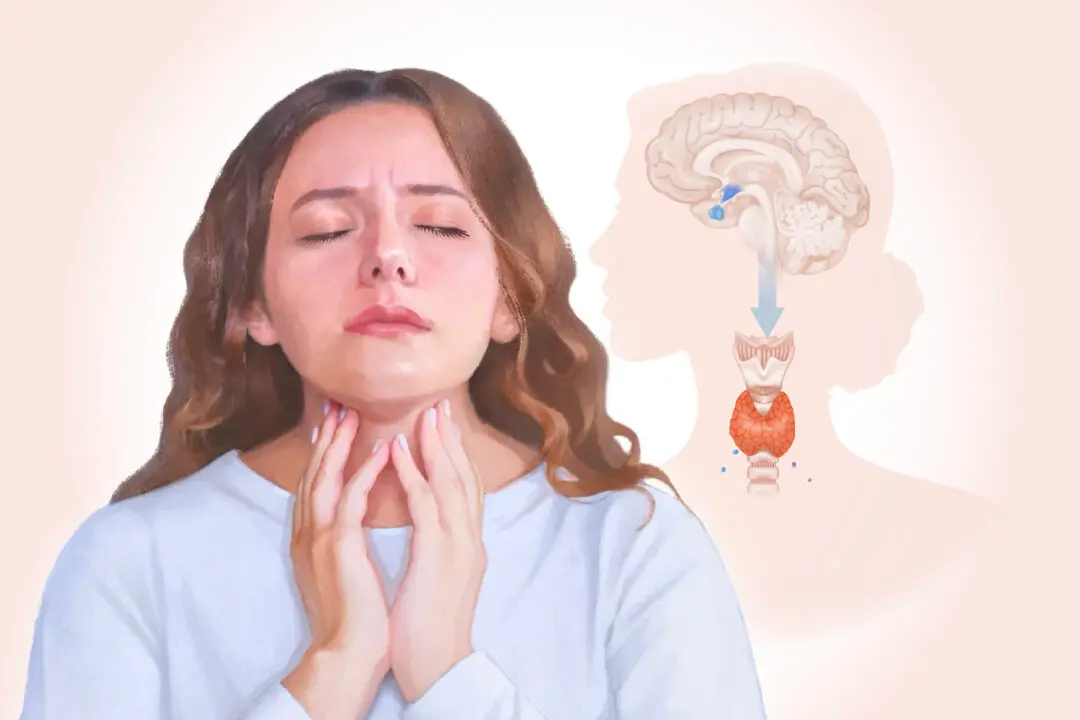
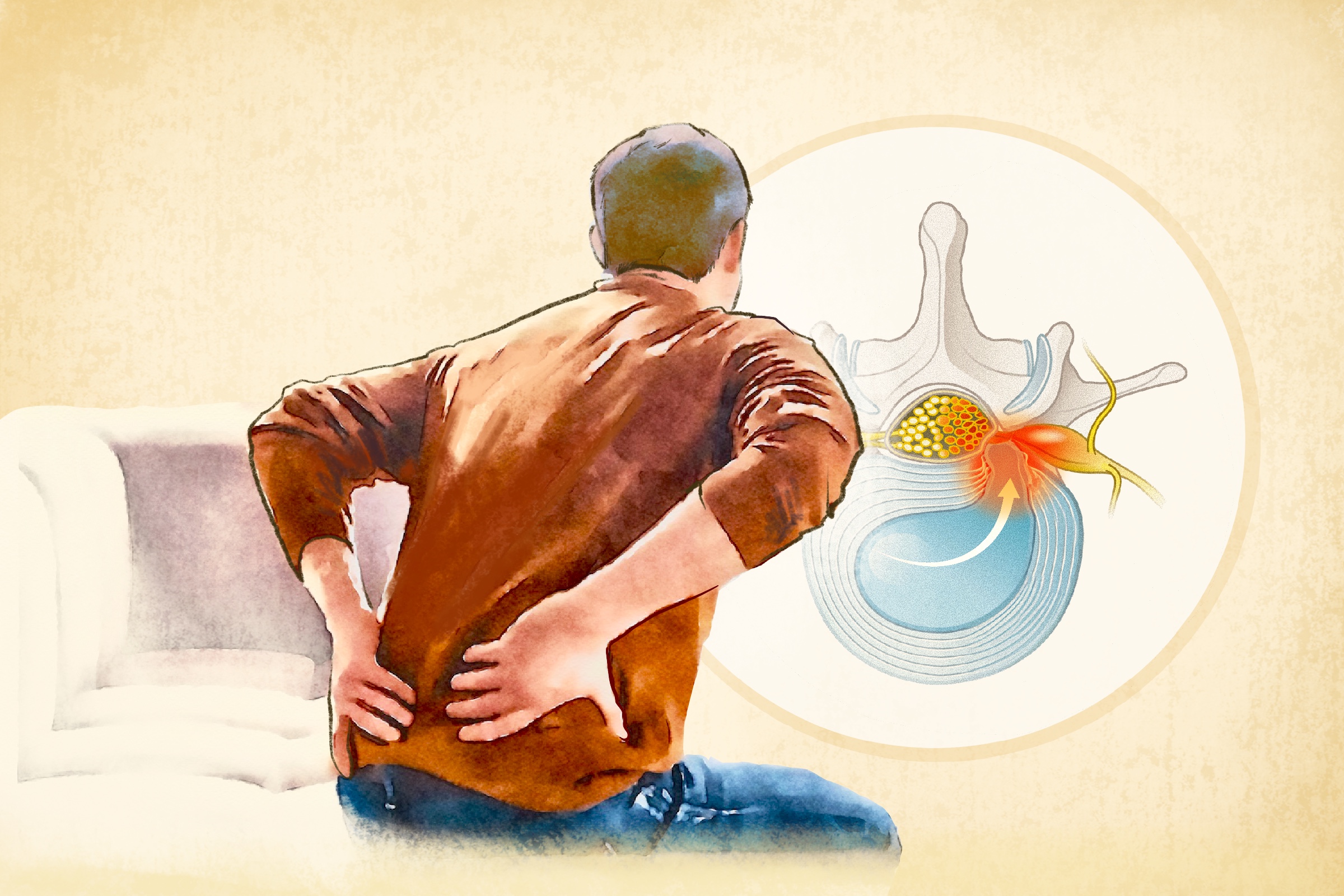
A herniated (slipped) intervertebral disk is a spinal condition where the annulus fibrosus (the outer layer of a spinal disk) becomes damaged, allowing the nucleus pulposus (the inner gel-like core) to protrude through the weakened area. This displacement can place pressure on nearby nerves or the spinal cord, potentially causing pain and impairing spinal cord function.
Approximately 2 percent to 3 percent of Americans experience a herniated disk every year.