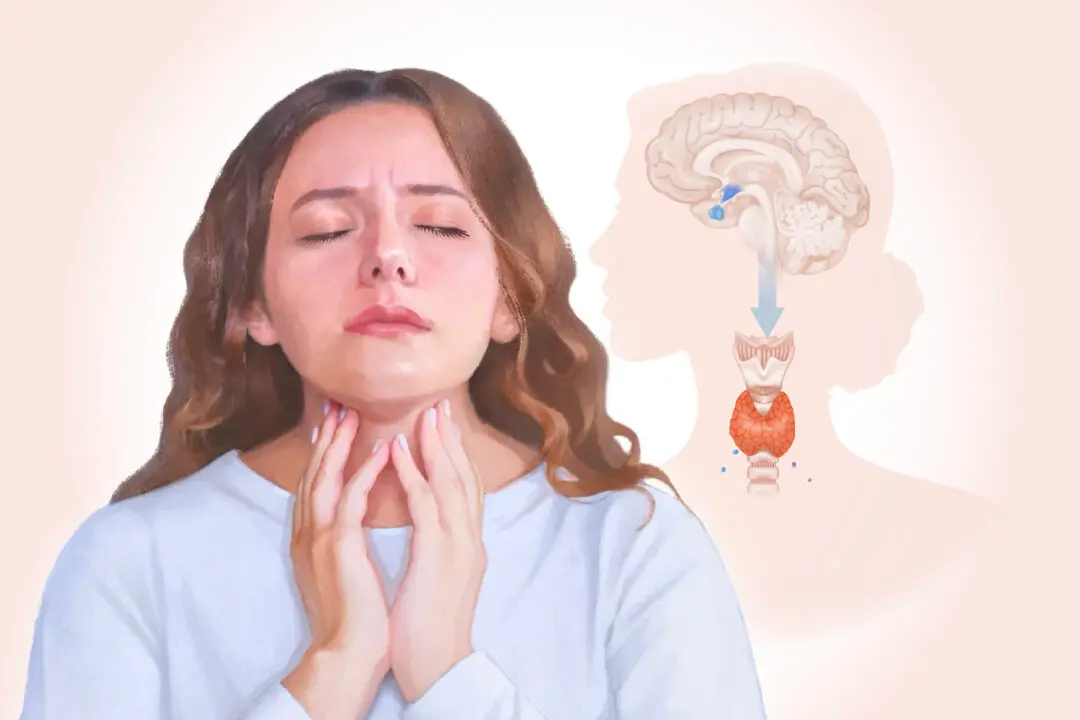
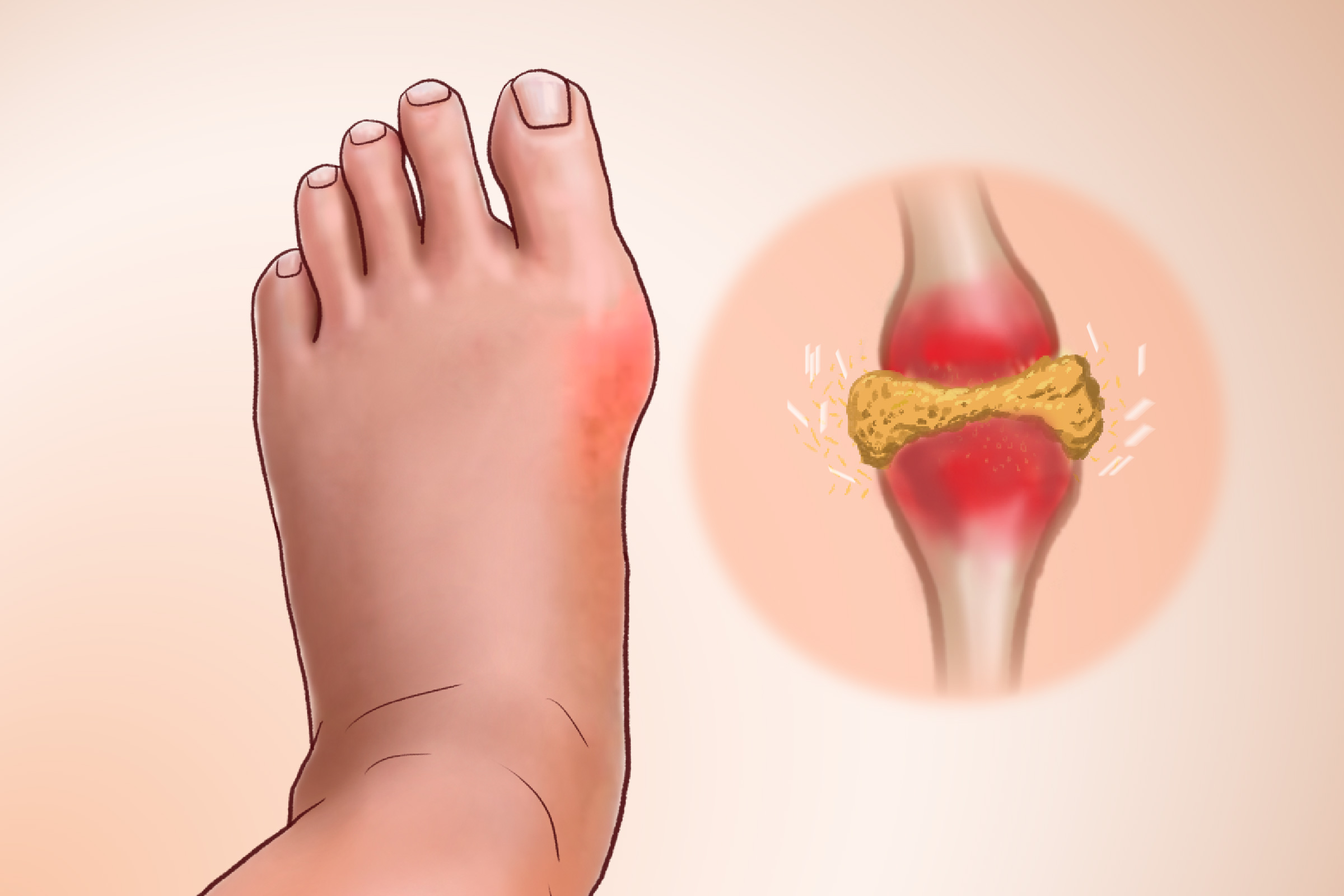
Once known as “the disease of kings” due to its association with overindulgence in rich foods and alcohol, gout is a form of arthritis characterized by sudden, painful inflammation in the joints. However, contrary to its aristocratic reputation, gout can affect people from all walks of life.
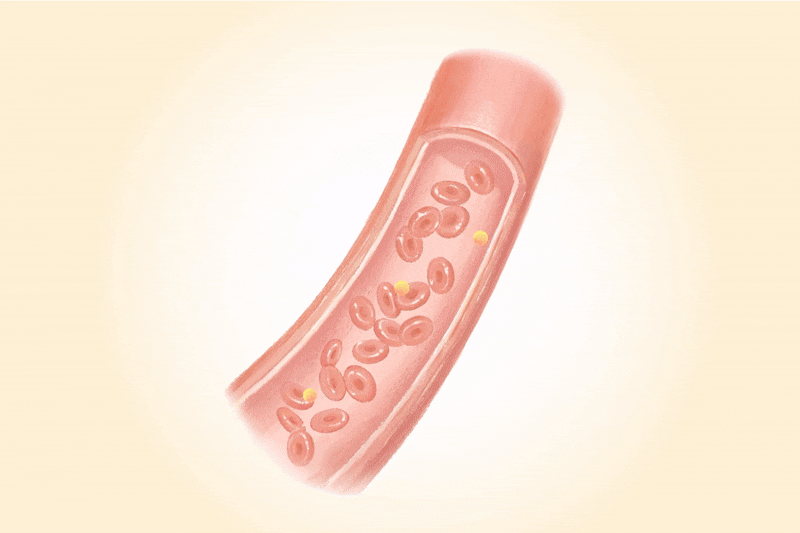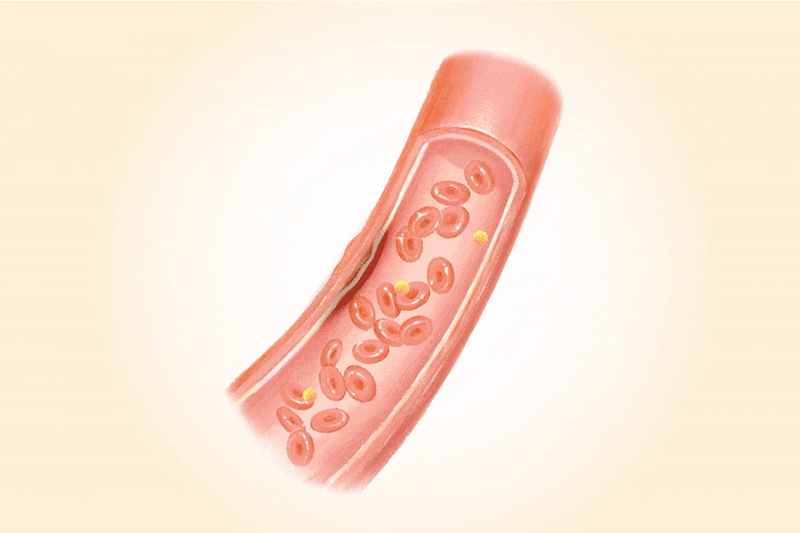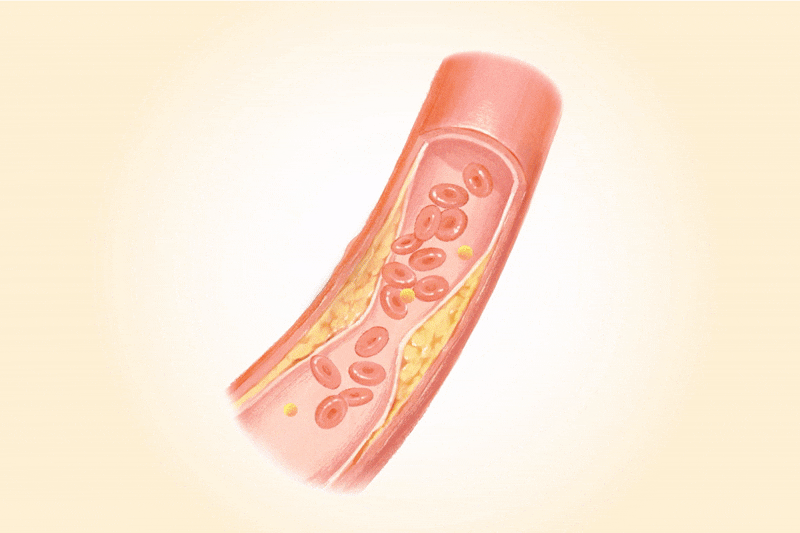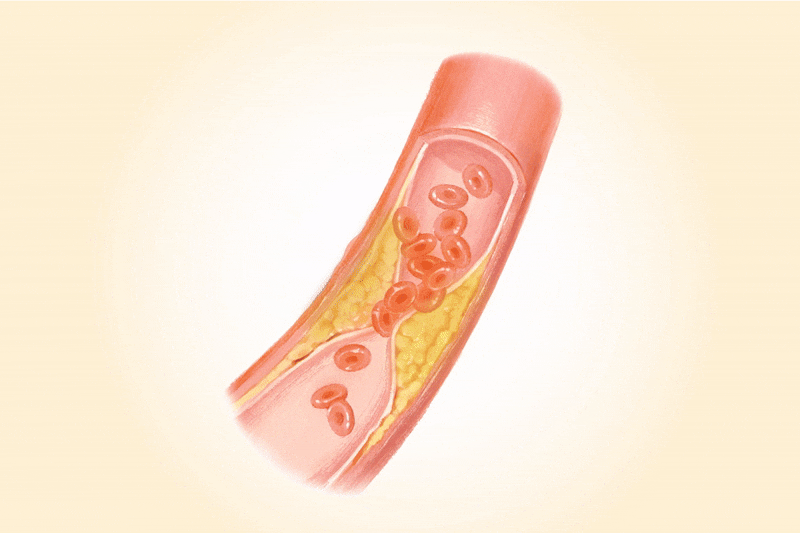
People with gout are more likely to have chronic kidney disease, metabolic conditions, and cardiovascular disease, and a 2019 study found gout to be associated with a 17 percent higher risk of death from all causes overall. The condition is now estimated to affect 1 in 25 American adults—and this number continues to rise, driven in part by the obesity epidemic.