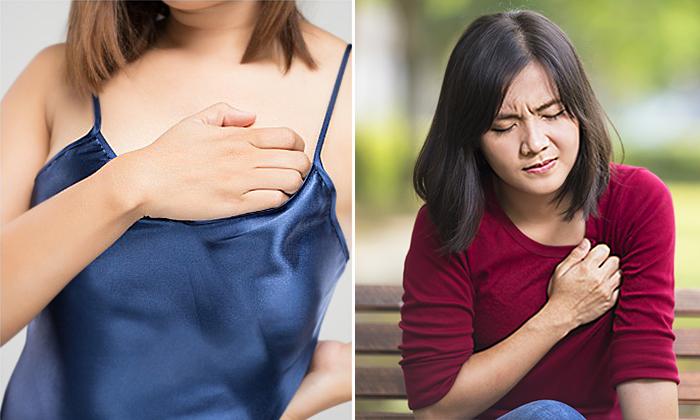
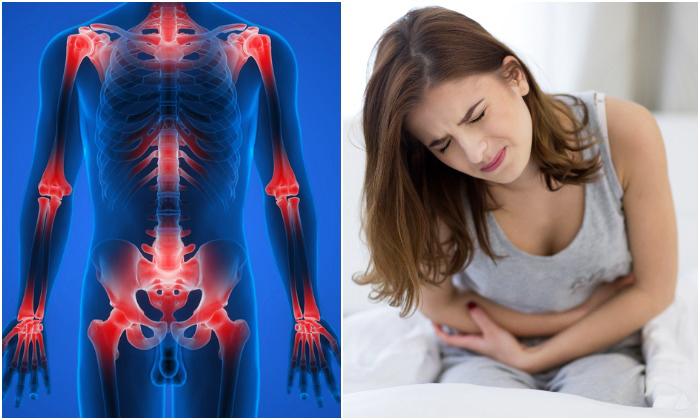
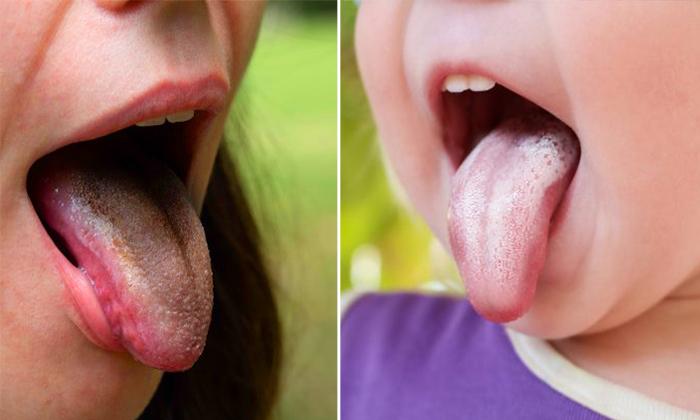
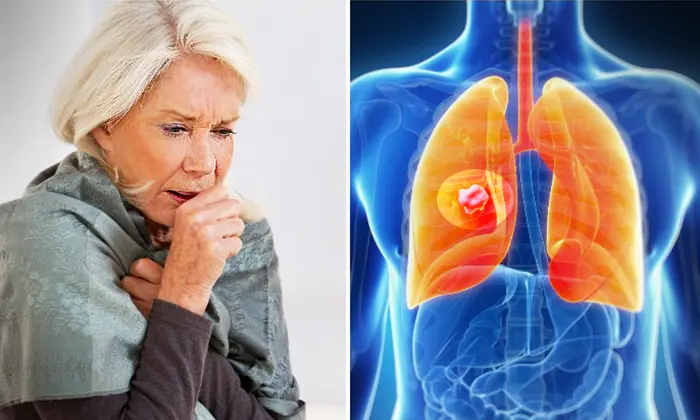
Inflammation is the body’s natural survival mechanism that typically indicates that your body is fighting off a disease or repairing damaged tissue. However, if inflammation persists for long periods of time, it may signal a problem in the body. Many serious health conditions are tied to chronic inflammation including heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, and even cancer.
Chronic inflammation may be the body’s response to lifestyle and environmental factors like poor dietary habits, stress, extra abdominal fat, insufficient sleep, or toxins from cigarette smoke or other types of pollution. Chronic inflammation has many negative effects. It can damage cells and organs, which can cause unpleasant symptoms, reduce quality of life, and even increase the risk of stroke.