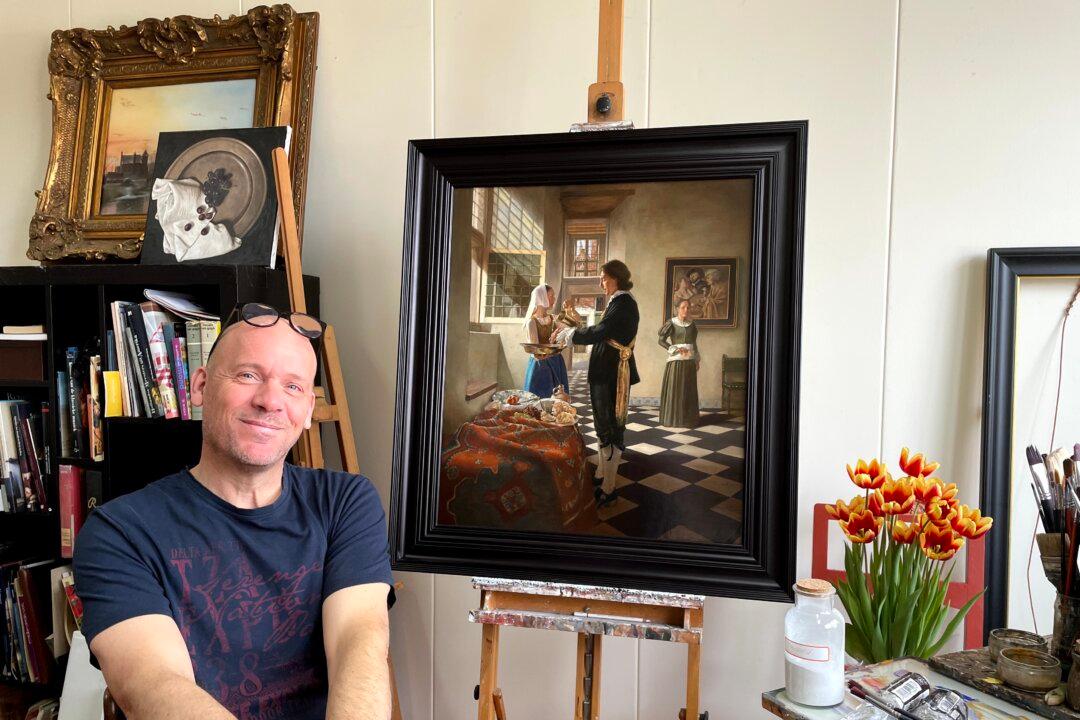
For over 25 years, Dutch artist Nard Kwast has poured his heart and soul into painting like 17th-century artists. His passion for the Golden Age of Dutch painting has paid off. He’s now a nationally known expert, who is passing his country’s art traditions to the next generation of Rembrandts.
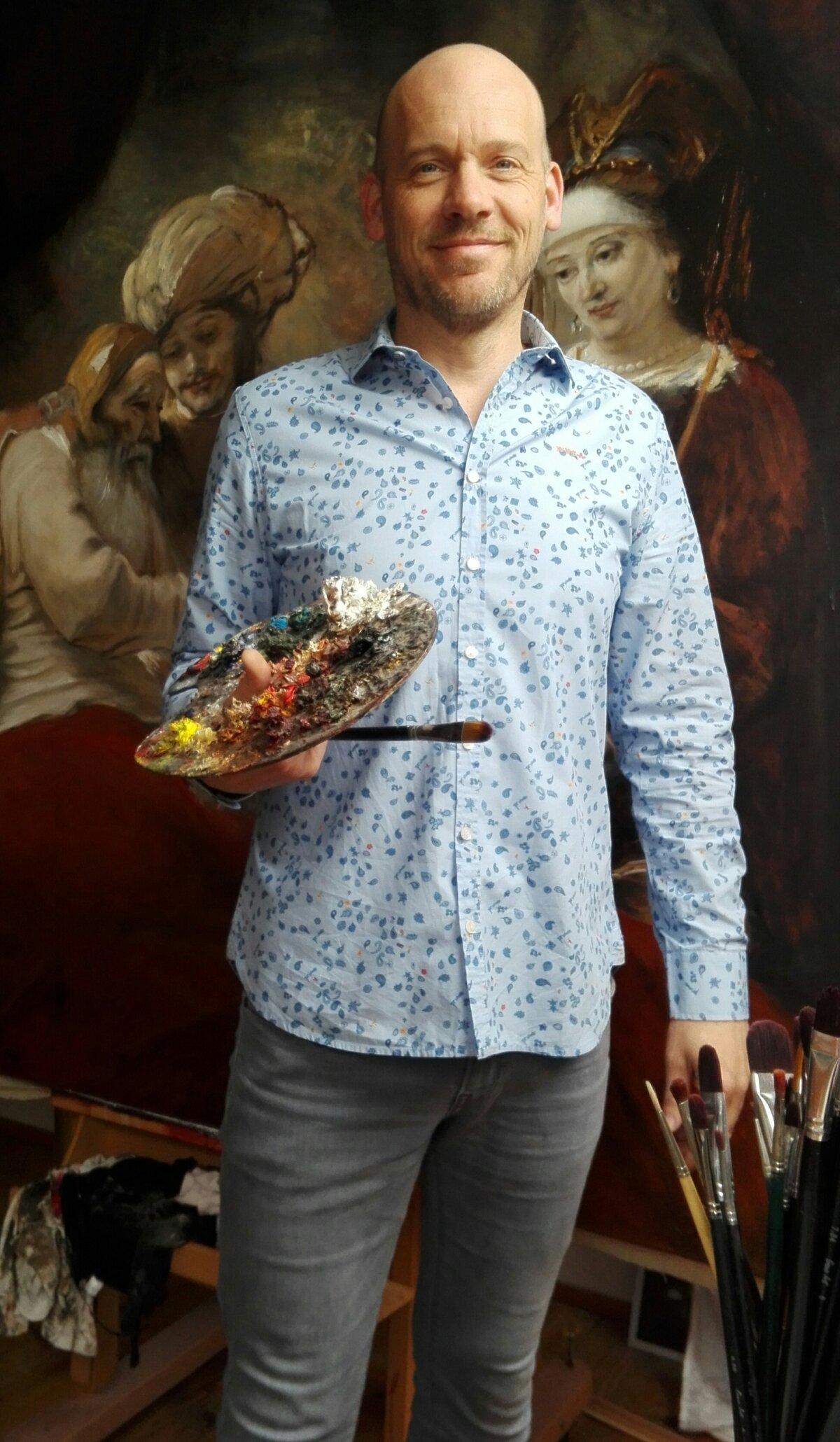
Artist Nard Kwast loves painting in the 17th-century style. He stands in front of a commissioned reproduction of Rembrandt's "Jacob Blessing the Sons of Joseph." Courtesy of Nard Kwast






