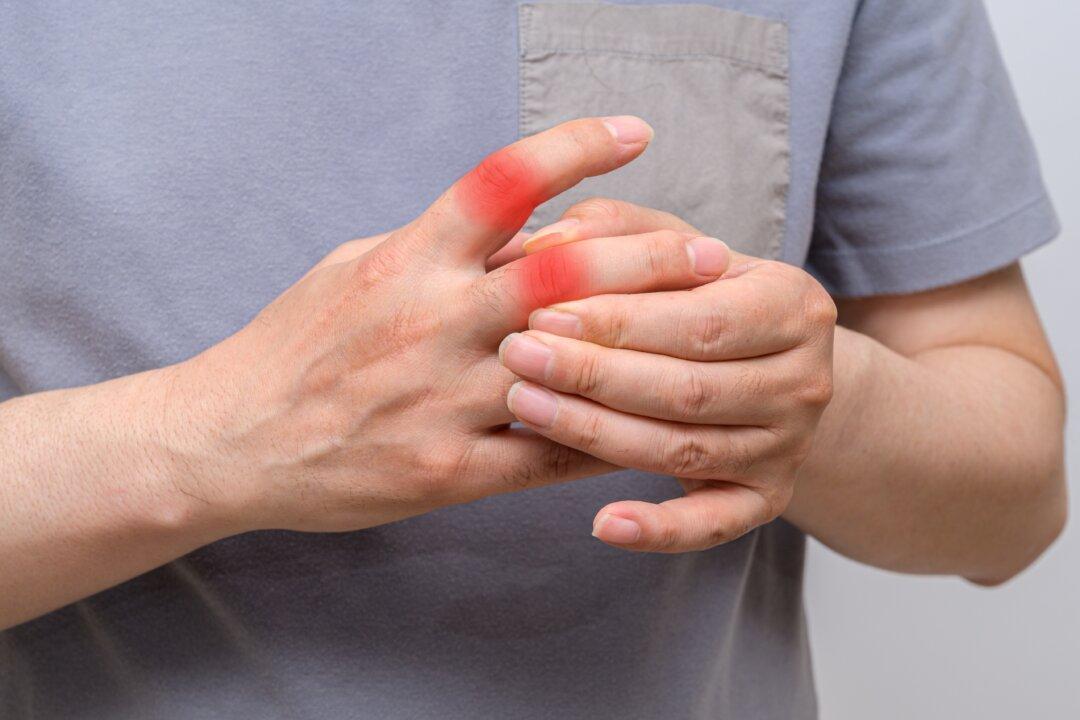
By David Jockers DC, MS, CSCS, Organic Lifestyle Magazine
Maca is a root vegetable belonging to the Brassica family of cruciferous vegetables. It is most similar to radishes and turnips in growth habits, size, and proportions. Maca is extremely rich in minerals with ample amounts of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, selenium, potassium, copper, and zinc. These are extremely important for healthy skin, bones, eyes, and joints. These minerals are also vital for effective cellular formation, communication, and regeneration.