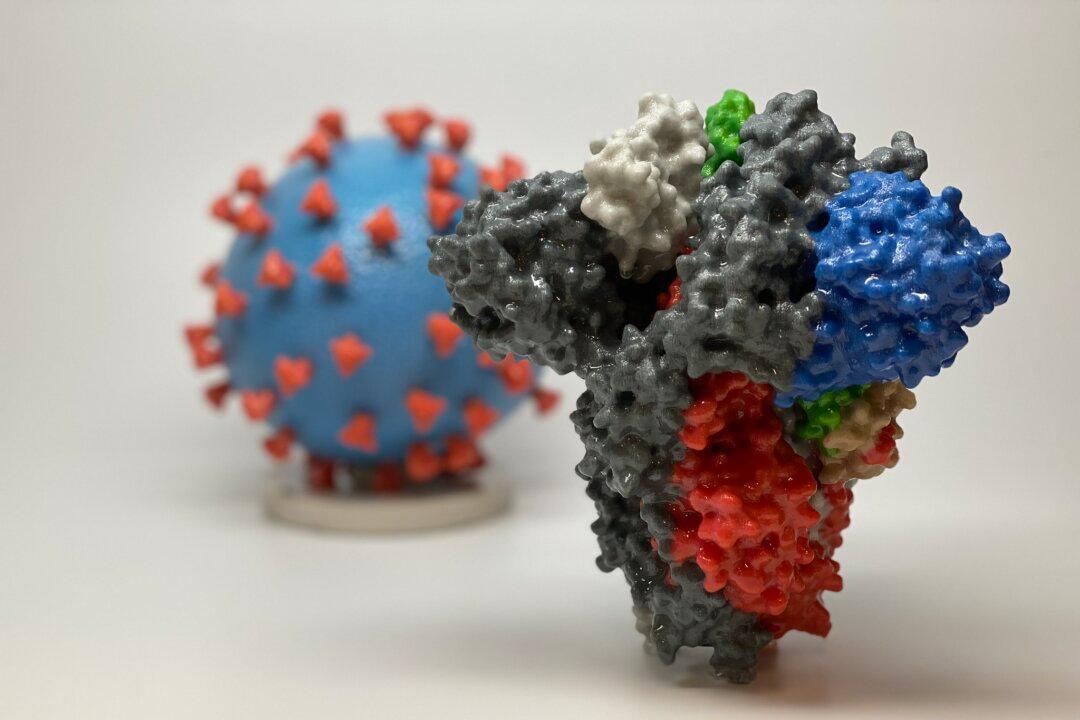
Several studies on saliva show that it has many beneficial properties including preventing viruses from binding to cells and promoting wound healing.
Saliva Prevents Virus Adherence to Human Cells
A study by a Japanese research team has shown that a specific protein in saliva has the function of preventing adherence of the CCP virus that causes COVID-19.On July 6, a research team from Osaka Public University, Japan published a study in The Journal of Biochemistry and the Journal of the United States National Library of Medicine, respectively, demonstrating that neutrophil-associated cationic proteins contained in saliva can prevent CCP (Chinese Communist Party) virus infection.