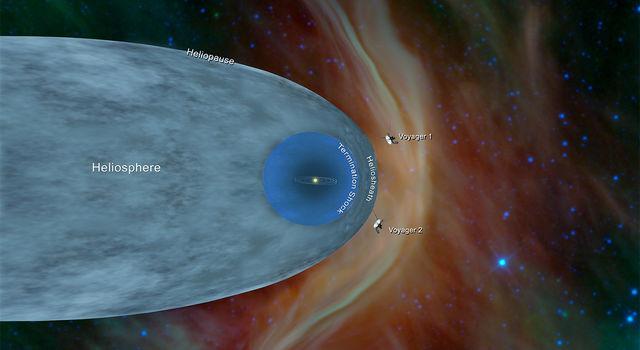
WASHINGTON—Voyager 2, a NASA probe launched in 1977 and designed for just a five-year mission, has become only the second human-made object to enter interstellar space as it continues its marathon trek billions of miles (km) from Earth, scientists said on Dec. 10.
Data from instruments aboard the spacecraft showed it crossed the outer edge of the heliosphere, a protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields produced by the sun, on Nov. 5, the U.S. space agency said.