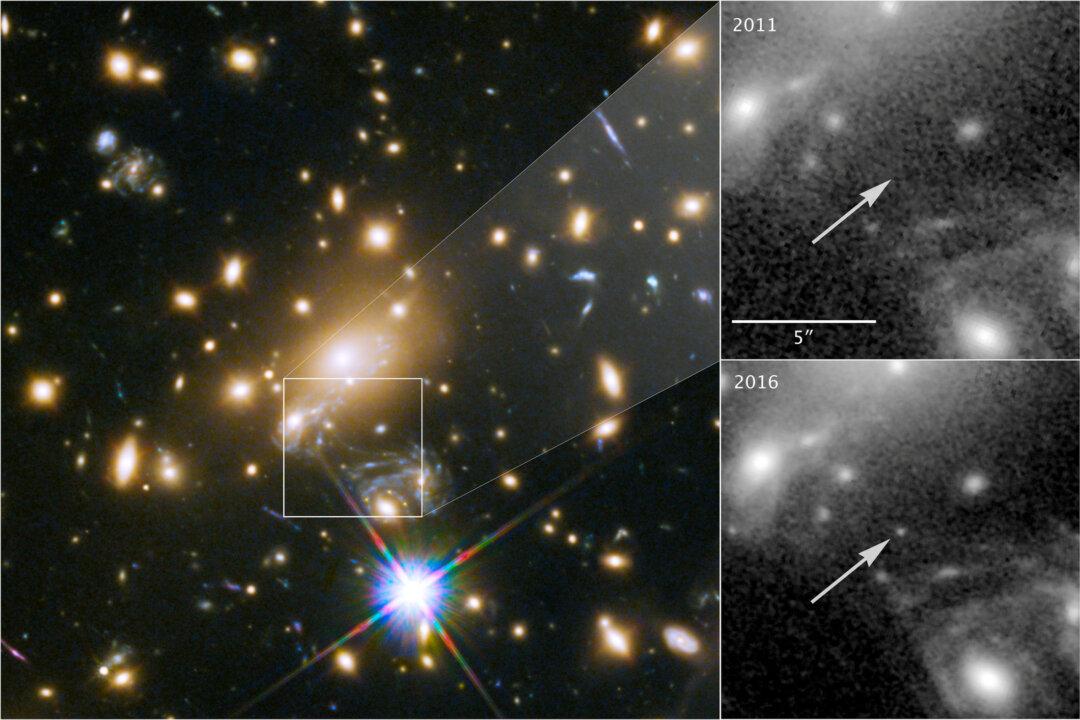
WASHINGTON—Scientists have detected the most distant star ever viewed, a blue behemoth located more than halfway across the universe and named after the ancient Greek mythological figure Icarus.
Researchers said on Monday they used NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope to spot the star, which is up to a million times more luminous and about twice as hot as our sun, residing 9.3 billion lights years away from Earth. It is a type of star called a blue supergiant.