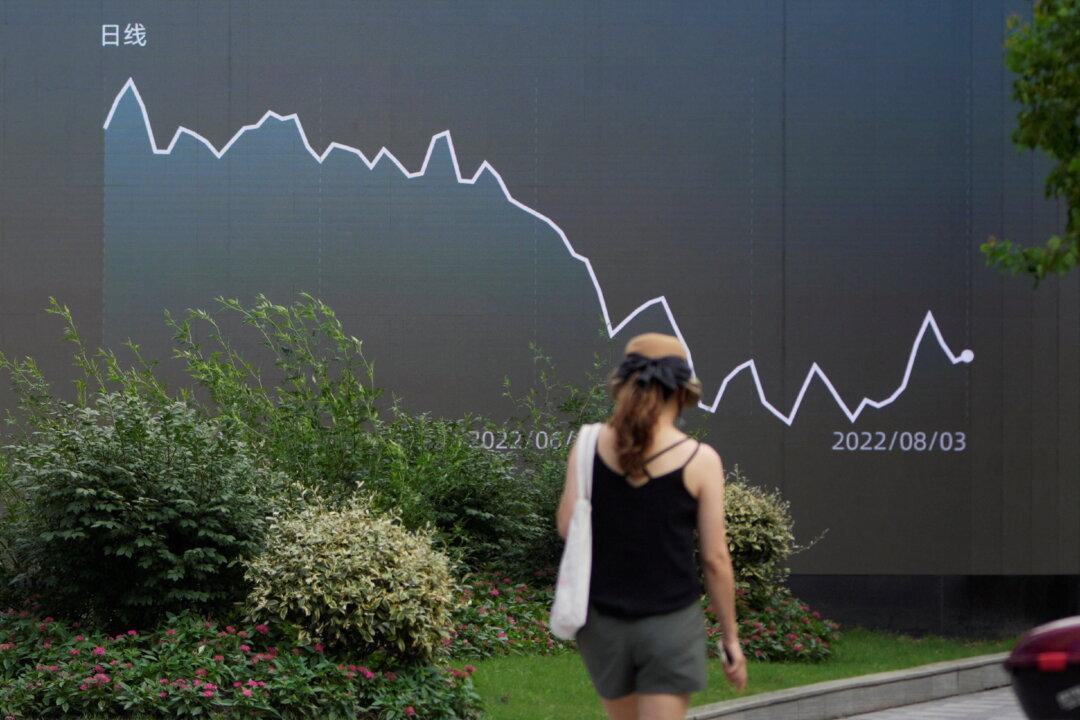
LONDON—Global equities fell on Tuesday as weak service sector data rekindled worries over China’s sputtering post-pandemic economy, while Australia’s central bank kept interest rates unchanged, pushing the Australian dollar lower.
European equity indexes opened in the red, with the pan-European benchmark STOXX 600 dropping 0.8 percent and Germany’s DAX, France’s CAC 40 and Britain’s FTSE 100 all nursing losses of between 0.6 percent–1.2 percent.