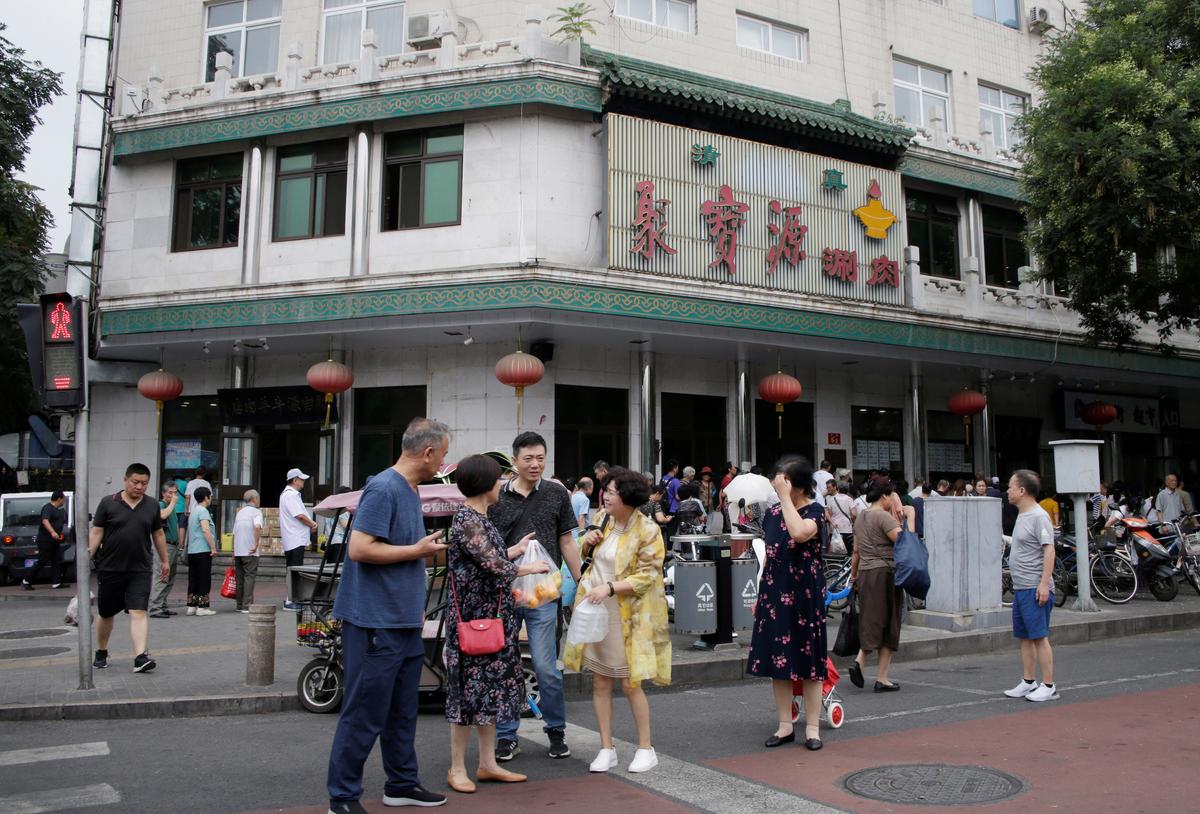
BEIJING—Authorities in the Chinese capital have ordered halal restaurants and food stalls to remove Arabic script and symbols associated with Islam from their signs, part of an expanding national effort to “sinicize” its Muslim population.
Employees at 11 restaurants and shops in Beijing that sell halal products told Reuters that officials had told them to remove images associated with Islam, such as the crescent moon and the word “halal” written in Arabic, from signs.
Government workers from various offices told one manager of a Beijing noodle shop to cover up the “halal” in Arabic on his shop’s sign, and then watched him do it.
“They said this is foreign culture and you should use more Chinese culture,” said the manager, who, like all restaurant owners and employees who spoke to Reuters, declined to give his name due to the sensitivity of the issue.
The campaign against Arabic script and Islamic images marks a new phase of a drive that has gained momentum since 2016, aimed to ensure that religions conform with mainstream Chinese culture.
The campaign has included the removal of Middle Eastern-style domes on many mosques around the country in favor of Chinese-style pagodas.

China, home to 20 million Muslims, officially guarantees freedom of religion, but the government has campaigned to bring the faithful into line with Communist Party ideology.
It’s not just Muslims who have come under scrutiny. Authorities have shut down many underground Christian churches, and torn down crosses of some churches deemed illegal by the government.
But Muslims have received particular attention since a riot in 2009 between mostly Muslim Uyghur people and majority Han Chinese in the far western region of Xinjiang, home to the Uyghur minority.
In response, China launched what it described as a crackdown on terrorism in Xinjiang and to stamp out religious extremism. Officials have warned about creeping Islamisation, and have extended tighter controls over other Muslim minorities.
Now, the Chinese regime is facing intense criticism from Western nations and rights groups over its policies, in particular mass detentions and surveillance of Uyghurs and other Muslims there.

‘New Normal’
Analysts say the ruling Communist Party is concerned that foreign influences can make religious groups difficult to control.“Arabic is seen as a foreign language and knowledge of it is now seen as something outside of the control of the state,” said Darren Byler, an anthropologist at the University of Washington who studies Xinjiang.
“It is also seen as connected to international forms of piety, or in the eyes of state authorities, religious extremism. They want Islam in China to operate primarily through Chinese language,” he said.
Kelly Hammond, an assistant professor at the University of Arkansas who studies Muslims of the Hui minority in China, said the measures were part of a “drive to create a new normal.”
Beijing is home to at least 1,000 halal shops and restaurants, according to the Meituan Dianping food delivery app, spread across the city’s historic Muslim quarter as well as in other neighborhoods.
It was not clear if every such restaurant in Beijing has been told to cover Arabic script and Muslim symbols. One manager at a restaurant still displaying Arabic said he'd been ordered to remove it but was waiting for his new signs.

Several larger shops visited by Reuters replaced their signs with the Chinese term for halal—“qing zhen”—while others merely covered up the Arabic and Islamic imagery with tape or stickers.
The Beijing government’s Committee on Ethnicity and Religious affairs declined to comment, saying the order regarding halal restaurants was a national directive.
“Currently, our country’s halal food regulation is managed locally, every local government’s relevant department administers it according to the local dietary habits and customs,” Zha Xi, an official from the National Ethnic Affairs Commission, told Reuters on Aug. 1.
While most shopkeepers interviewed by Reuters said they didn’t mind replacing their signs, some said it confused their customers and an employee at a halal butcher shop accused authorities of “erasing” Muslim culture.
“They are always talking about national unity, they’re always talking about China being international. Is this national unity?”