Baidu Inc.’s standing amongst China’s elite internet triumvirate is on shaky ground as the company battles slowing sales growth, regulatory uncertainty, and an ongoing cash burn from diversification.
The company has a near monopoly on China’s internet search business after Google exited in 2010. But the business environment is deteriorating and its efforts to diversify away from search—which generates over 90 percent of Baidu’s revenues—have not yielded returns. While second-quarter sales increased 10 percent, profits dropped 36 percent year over year, the biggest quarterly decline in the company’s 11 year history as a publicly traded entity.
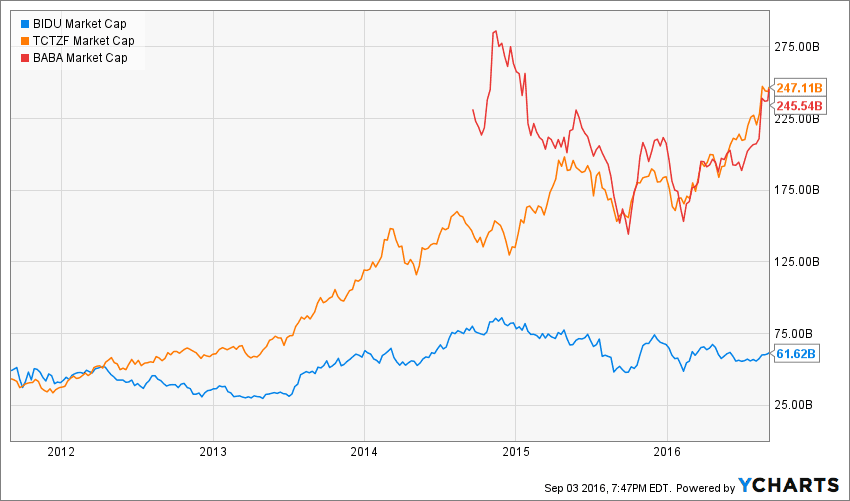
Baidu’s U.S.-listed ADR shares are down around 6 percent year-to-date. Its market capitalization is now dwarfed by other members of the “BAT”—China’s big three internet giants of Baidu, Alibaba Group, and Tencent Holdings.